The Connection Between Hormones and Hair Loss

The Connection Between Hormones and Hair Loss
Hormonal Causes of Hair Loss
Explore how hormonal imbalances, including fluctuations in androgens, estrogen, and thyroid hormones, contribute to hair loss. Understand the science behind hormonal hair loss and discover effective treatment options.
Androgens and Hair Loss (DHT and Testosterone)
Androgens are male hormones, with testosterone and its stronger form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Oestrogen and Progesterone Imbalance
Oestrogen and progesterone are female hormones that help keep hair in the anagen phase
Thyroid Hormones (Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism)
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Abnormal thyroid hormone levels
When Hormones Harm: Uncovering the Root Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss is a concern that affects millions of people across the UK, regardless of age or gender. For some, it may begin as a slight thinning around the temples or a patch at the crown, while for others, it manifests as a sudden shedding or gradual baldness. Although there are many contributing factors, one of the most significant and often overlooked is the role of hormones. Hormonal fluctuations can wreak havoc on the natural hair growth cycle, and understanding this connection is vital in identifying effective solutions.
This article explores how different hormones influence hair health, what conditions trigger hormonal imbalances, how these imbalances manifest, and the treatments available to help restore hair growth.
What Are Hormones and How Do They Affect Hair?
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system. They travel through the bloodstream to organs and tissues, regulating metabolism, growth, mood, and hair growth. Hair follicles are extremely sensitive to hormonal changes, and even slight shifts in hormone levels can alter the hair growth cycle.
The hair growth cycle consists of three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting). Hormonal imbalances can shorten the growth phase or prolong the resting phase, leading to increased shedding or delayed regrowth. Understanding which hormones play key roles is the first step in addressing hormone-related hair loss.
Hormonal Causes of Hair Loss: A Breakdown
Hormones don’t act in isolation. Various hormonal imbalances can lead to hair loss, and the underlying causes can differ between men and women.
1. Androgens and Hair Loss (DHT and Testosterone)
Androgens are male hormones, with testosterone and its stronger form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), being the most well-known. Both men and women produce androgens, though in different quantities. In those with a genetic predisposition, DHT connects with specific sites in the scalp’s hair roots, causing them to become smaller over time. This process is known as miniaturisation and is the leading cause of androgenetic alopecia, commonly referred to as male or female pattern baldness.
This condition often leads to the hairline gradually moving backwards or thinning at the crown in men. Women may notice a general thinning across the scalp without significant recession. Androgen sensitivity is largely hereditary, but hormonal changes, such as those during puberty, after childbirth, or during menopause, can trigger it.


- 2,453 Grafts
- 10 Months Post Op
2 .Oestrogen and Progesterone Imbalance
Oestrogen and progesterone are female hormones that help keep hair in the anagen phase. When levels of these hormones drop, particularly during menopause or after giving birth, hair may enter the resting phase prematurely and shed more easily.
Some women notice increased hair thinning when starting or stopping birth control pills or undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT). These fluctuations disrupt the body’s natural hormone balance and may contribute to temporary or long-term hair loss.
3 . Thyroid Hormones (Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism)
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Abnormal thyroid hormone levels—whether too low (hypothyroidism) or too high (hyperthyroidism)—can interfere with the natural hair growth cycle.
Hair may become dry, brittle, and prone to shedding. In some cases, hair loss occurs diffusely across the scalp. Autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are also associated with alopecia.


- 2,000Grafts
- 11 Months Post Op
4. Cortisol and Stress-Induced Hair Loss
Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, is vital for managing the “fight or flight” response. However, chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels and lead to telogen effluvium—a condition where large numbers a large number of hair follicles shift into the resting stage at the same time.
Unlike pattern baldness, telogen effluvium causes sudden, noticeable shedding across the scalp. Although typically temporary, it can become chronic if stress is not effectively managed.
Hormonal Hair Loss in Women: What You Need to Know
Women often find hair loss more emotionally challenging, largely because of societal expectations and cultural beauty norms. Understanding the hormonal triggers specific to women can help in finding tailored treatment.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age. It leads to elevated levels of androgens, which can cause scalp hair thinning while simultaneously increasing facial and body hair.
This paradoxical effect is distressing and difficult to manage without professional medical intervention. Lifestyle changes, medications like spironolactone, and hormonal treatments can help balance androgens and improve hair density. - Menopause and Hair Thinning
During menopause, oestrogen and progesterone levels decline significantly. This hormonal shift can increase sensitivity to DHT, resulting in thinner hair or wider partings on the scalp.
Some women opt for HRT to manage menopausal symptoms, which may also benefit hair health. Others explore natural remedies or use topical treatments like minoxidil to slow hair loss.
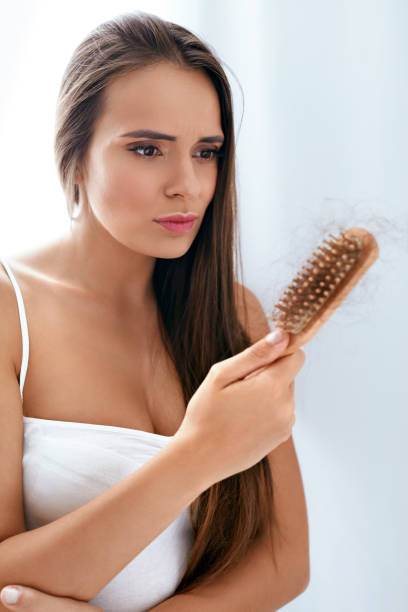

- Pregnancy and Postpartum Hair Loss
Pregnancy typically prolongs the anagen phase due to elevated hormone levels, leading to fuller, healthier hair. However, after childbirth, hormone levels rapidly decline, triggering telogen effluvium.
Hormonal Hair Loss in Men: Common Patterns and Causes
Due to higher androgen levels and genetic influence, men are more likely to experience visible hair loss earlier in life. Identifying the type and cause of hormonal hair loss can guide effective treatment.
1. Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Male Pattern Baldness and DHT Sensitivity

This is the most known cause of hair loss in men and is directly linked to DHT sensitivity. Hair typically recedes from the temples and thins at the crown, eventually leading to baldness if untreated.
Finasteride (a DHT blocker) and minoxidil can slow or reverse hair loss. Early intervention tends to yield the best results.
If your father, mother, or grandparents experienced hair loss, there’s a strong likelihood you may too. Your genetic makeup determines how sensitive your follicles are to DHT.
2. Hormonal Imbalances in Young Men
Hormonal Triggers of Hair Loss in Young Men

Younger men may experience hair loss due to hormonal changes during puberty, excessive use of anabolic steroids, or medical conditions affecting hormone production.
Testosterone therapy, often prescribed for low libido or energy levels, can also exacerbate hair loss if not properly managed.

3. Diagnosing Hormonal Hair Loss
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in Hair Loss Treatment
Proper diagnosis is essential before beginning any treatment. Hormonal hair loss often resembles other types, making lab tests and clinical evaluations crucial.
4. Signs and Symptoms to Look Out For
Recognizing the Signs of Hormonal Hair Loss

Common indicators include diffuse thinning, patchy hair loss, or excessive shedding. Women may notice irregular periods or acne, while men might experience reduced muscle mass or libido changes.
5. Blood Tests and Hormonal Panels
Hormone Testing for Targeted Hair Loss Treatment
Healthcare providers may test for levels of thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4), sex hormones (testosterone, DHEA, oestrogen), and cortisol. Identifying imbalances helps tailor treatment plans that address the root cause.
Treatment Options for Hormonal Hair Loss
Once the hormonal imbalance is identified, several treatment avenues may be pursued depending on the individual’s condition and preferences.
1. Medical Treatments
- Finasteride: Reduces DHT levels and slows hair loss in men.
- Minoxidil: Topical treatment that stimulates hair growth in both men and women.
- Spironolactone: An anti-androgen medication often used for female hair loss.
- Hormone Therapy: Includes HRT or thyroid medication to address underlying hormonal issues.
2. Natural and Lifestyle-Based Solutions
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in iron, zinc, and omega-3s supports hair growth.
- Stress Reduction: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and adequate sleep help regulate cortisol.
- Supplements: Biotin, vitamin D, and magnesium may improve hair health, especially when deficiencies occur.
3. Advanced Procedures: PRP, Microneedling & Hair Transplants
- PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma injections stimulate dormant follicles.
- Microneedling: Encourages collagen production and hair regeneration.
- Hair Transplants: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and other techniques provide long-term solutions, especially for pattern baldness.
Preventing Hormonal Hair Loss: Long-Term Strategies
While not all hair loss is preventable, maintaining hormonal balance can significantly reduce the risk. Regular exercise, healthy eating, stress management, and routine health check-ups play a role.
Early detection is key. By recognising the signs and addressing them promptly, you can preserve hair density and minimise long-term loss.

Why Choose Merchant City Medical Group
for Hair Loss Treatment
Professional expertise is invaluable when it comes to managing hormone-related hair loss. Merchant City Medical Group is a trusted provider of advanced hair restoration treatments in the UK.
- Expertise in Hormonal Hair Loss
Our team of specialists understands the intricate link between hormones and hair loss. We conduct thorough consultations, including blood tests and hormone panels, to identify the root causes of your hair concerns. - Advanced Hair Restoration Solutions
We offer cutting-edge procedures such as FUE hair transplants, PRP therapy, and microneedling, all performed in a comfortable, clinical environment. Whether you’re struggling with male pattern baldness or postpartum shedding, we tailor treatments to suit your needs. - Patient-Centric Approach
From the moment you walk into our clinic, you’re treated as an individual. We listen, assess, and recommend only the most appropriate solutions based on your unique situation. Our patient testimonials speak volumes about our commitment to quality care and long-term results.
Conclusion
Hormones play an important role in hair health; hair loss can occur when out of balance. Understanding the hormonal causes of hair thinning and seeking professional guidance can help you regain control and confidence.
Merchant City Medical Group is here to help you on that journey. With expert diagnosis and personalised treatment plans, restoring your hair is not just possible—it’s achievable. Book a free consultation today and take the first step towards a fuller, healthier head of hair.
Understanding the role of DHT and how it affects your follicles is key to regaining control. With proper diagnosis, tailored treatment, and expert support from clinics like Merchant City Medical Group, restoring your hair and confidence is entirely within reach.
Excellence Record
- 30+ Years of combined experience
- 10 + Experts
- 1000 + Satisfied Patients