What Causes Hair Loss in Men? A Comprehensive Guide
What Causes Hair Loss in Men? A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the causes of hair loss in men with our comprehensive guide. Understand factors, treatments, and prevention tips. Whether the cause is genetics, stress, or something else entirely, knowing the cause is key to finding the right solution. In this guide, we’ll discuss the most common reasons men experience hair loss and offer insights and solutions that might surprise you. Ready to uncover what’s going on with your hair? Let’s dive into the factors that could be at play and what they mean for you.

What Causes Hair Loss in Men?
Hair loss is more common than you might think, and if you’re noticing a little less up top, you’re not alone. Understanding what’s behind this change can be the first step to taking control. Whether the cause is genetics, stress, or something else entirely, knowing the cause is key to finding the right solution. In this guide, we’ll discuss the most common reasons men experience hair loss and offer insights and solutions that might surprise you. Ready to uncover what’s going on with your hair?
Let’s dive into the factors that could be at play and what they mean for you.
Understanding Hair Growth
Hair develops in four unique stages. The final step involves shedding old hair for new hair growth. Certain situations disrupt the hair growth cycle. Although hair growth and loss appear simple, the hair growth cycle is separated into four distinct stages. Researchers have extensively studied the stages of hair development to gain a deeper understanding of hair growth. This knowledge helps identify ways to prevent or treat premature hair loss . The first three phases—anagen, catagen, and telogen—deal with hair development and maturation and the activity of the hair follicles that create individual hairs. During the last, or exogen, phase, “old” hair loses, but new hair is usually ready to replace it. Each phase has its timetable that can be influenced by age, nutrition, and overall health. This implies that you can take steps to help guarantee that your hair follows a healthy growth cycle. Let’s look into the details of each hair growth.
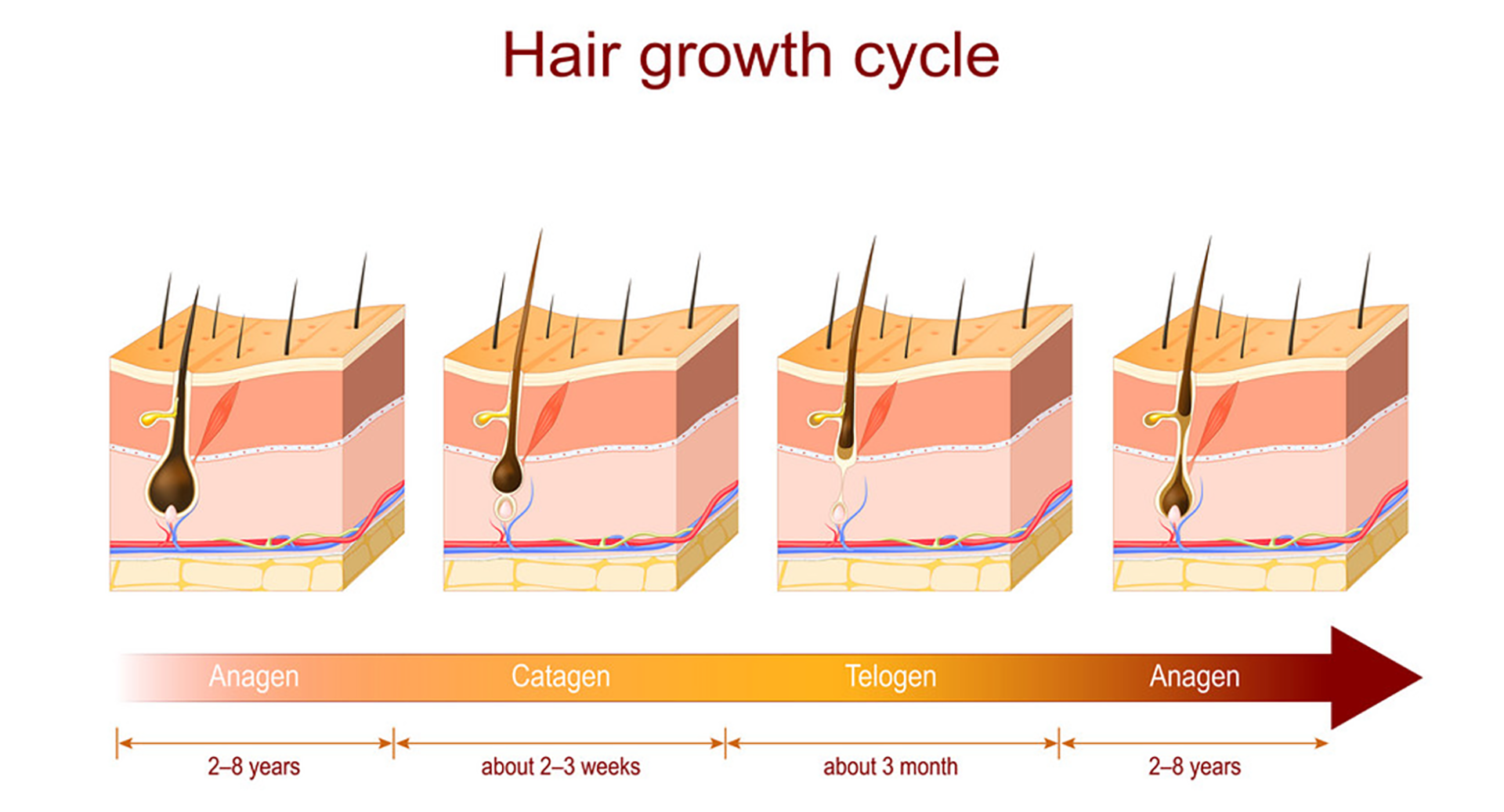
- Anagen: The Hair Growth Stage
The anagen phase marks the start of the hair growth cycle. It is the longest phase, lasting 3 to 5 years for the hairs on your head, yet for some people, a single hair may grow for seven or more years. Fortunately, the anagen phase varies with each type of hair. For example, the anagen phase for brow and pubic hair is substantially shorter than that for scalp hair. During the anagen phase, hair follicles produce hair that develops until it is cut or falls out. Around 90% of the hairs on your head are typically in the anagen phase at any given moment. - Catagen: The Transition Stage
The catagen phase is after the anagen phase and generally lasts about ten days.
Hair follicles contract and development slows throughout this chapter.The hair separates from the base of the hair follicle but remains in situ throughout its last days of growth. Only about 5% of your hair is currently in the catagen phase.
- Telogen: The Resting Stage
The telogen period normally lasts three months. This phase affects roughly 10 to 15% of the hair on your head. During the telogen phase, hairs do not develop or fall out.It is also when new hairs grow in follicles that have just produced hairs during the catagen phase. Some health experts refer to the telogen phase as the shedding phase, although many scientists separate it into two parts: telogen and exogen.
- Exogen: The Shedding Phase
The exogen phase is simply an extension or subset of the telogen stage of hair growth. During the exogen phase, hair sheds off the scalp, typically aided by washing and brushing. Losing 50-100 hairs daily during the exogen phase is common.During the exogen phase, which might last between 2 and 5 months, new hairs grow in the follicles while old ones fall out.
Why Genetic Factors Cause Hair Loss in Men
Genetics greatly impacts how much hair loss you may experience as you age.
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
When your genetics cause hair loss, it occurs in a predictable pattern often called male pattern baldness (MPB).
For men, MPB manifests as an M-shaped recession at the front of the scalp, typically beginning in their 20s or 30s.By the age of 80, around 80% of men will have MPB. Androgenetic alopecia, or MPB and FPB, is the most prevalent cause of hair loss.
- DHT Sensitivity and Hair Follicle Shrinkage
Another reason genetics plays a role in hair loss is the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
This hormone binds to receptors in the follicles, shrinking and shortening the hair growth cycle, leading to gradual thinning and eventual hair loss.

- Inherited Traits Genetics determines your hair’s texture, density, and growth patterns. The traits you inherit from your parents can dictate whether your hair is thick or thin, straight or curly, and how quickly or slowly it grows. These inherited characteristics also influence your hair’s resilience to environmental factors and aging. Over time, these genetic traits can contribute to one’s sensitivity to hair thinning or loss. Understanding one’s genetic makeup helps one anticipate potential hair-related changes as one ages.


Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Hormonal abnormalities, particularly those involving testosterone and thyroid hormones, can substantially impact hair growth and loss in men.
- Thyroid CausesThyroid dysfunction might cause you to shed hair or cease growing hair completely. Fortunately, this is rarely permanent. However, it can be a common symptom of your thyroid’s hormone production not operating properly.
Unlike other types of baldness, thyroid-related hair loss affects not just the scalp but also the brows, pubic hair, and hair on other body regions. It can also be caused by some autoimmune illnesses, which frequently accompany thyroid issues (more on that later). Hair loss is usually reversed if thyroid hormone levels are normalised.
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Causes Hair Loss in MenTestosterone is a vital hormone that regulates deeper voices, muscle growth, and sex drive, among other male characteristics. However, the enzyme 5-alpha reductase can change testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), negatively affecting hair health.
DHT is a more potent form of testosterone, and while it’s necessary for certain bodily functions, it can also have a downside. DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, shrinking and weakening them over time. This process gradually leads to thinner hair, reduced hair growth, and hair loss, particularly in those genetically predisposed to sensitivity to DHT.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Certain lifestyle choices, such as diet, stress, smoking, and exposure to environmental pollutants, can contribute to hair loss in men by affecting hair health and growth cycles.
Let’s look at the details
Stress Causes Hair Loss
You may feel overwhelmed if work has been extremely hectic or you have an overdue college assignment. It’s crucial to understand that this is a fully normal reaction. The Mayo Clinic states that certain degrees of stress can be a healthy motivator.
However, if you see that your stress levels are interfering with your ability to complete your daily responsibilities, it’s probable that they also cause your hair loss. High stress levels can result in three common kinds of hair loss: telogen effluvium, trichotillomania, and alopecia areata.
If you feel stress is the cause, manage it by spending time with friends, getting outside for fresh air, and giving yourself the TLC you deserve. Fortunately, stress-related hair loss is typically temporary.





Diet and Nutrition
Nutritional deficiencies can impact hair structure and development. The effects on hair growth include acute telogen effluvium (TE), a well-known result of abrupt weight loss or decreased protein consumption, and the generalised alopecia found in niacin deficiency.
Iron deficiency (ID) is the most frequent dietary deficit worldwide and a well-known cause of hair loss. However, the degree to which ID may lead to hair loss is uncertain.
While the mechanism by which iron affects hair growth is unknown, hair follicle matrix cells are among the most rapidly dividing cells in the body, and ID may contribute to hair loss by acting as a cofactor for ribonucleotide reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme for DNA synthesis. Furthermore, many genes have been found in the human hair follicle, some of which may be regulated by iron.
Zinc is an important mineral for hundreds of enzymes and transcription factors that control gene expression. While the specific mechanism of action is unknown, one idea is that zinc acts as a key component of multiple metalloenzymes involved in protein synthesis and cell division. Another explanation is zinc’s involvement in the Hedgehog signaling pathway, an important component of the pathways that drive hair follicle formation. Therefore, its deficiency leads to hair loss in most people.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to nutritional deficits or malabsorption. Lack of zinc, copper, or protein can cause hair shedding. As mentioned earlier, Iron may contribute to hair loss in certain people. People who drink heavily may not get adequate nutrients due to a bad diet. In other circumstances, alcohol interferes with how the body digests and uses food.
On the other hand, social drinking and smoking can often go hand in hand. Smoking is linked to skin concerns such as wrinkles. Nicotine, along with other compounds in cigarettes, affects the skin and hair. It can constrict blood vessels and impair blood flow, preventing the skin from receiving adequate oxygen and nutrients. This eventually leads to aging skin developing roughness that makes one scratch the scalp.
Tobacco smoke contains around 4,000 compounds that can destroy collagen and elastin, causing drooping skin and accelerated ageing. One study especially investigated the link between smoking and baldness. It discovered a substantial relationship between the two. This is most likely due to smoking’s effects on the hair itself. It can harm the hair follicles and disrupt other aspects of the hair growth cycle.




Environmental Pollutants
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), outdoor air pollution kills around 4.2 million people yearly. The WHO also estimates that over 90% of the world’s population lives in polluted areas. Pollutants in surface and groundwater and other minerals, such as those found in hard water, cause hair follicles to dry out, crack, and thin.
Pollution has also been related to oily, itchy scalp and dandruff, which are fairly frequent symptoms in the general population. While there could be a much simpler reason, it is crucial to remember, particularly if one lives in a large industrial city, that pollution could be the fundamental cause.
If left untreated, this inflammation can cause irreversible hair loss.
Medical Conditions Cause Hair Loss in Men
Different medical conditions, from autoimmune disorders to chronic illnesses, may lead to hair loss in men. Understanding these conditions is crucial for diagnosing the underlying cause and finding the most effective treatment.
Certain Medications and Treatment
Some anticoagulants (medications that prevent blood from thickening or “clotting”) and several chemotherapy agents used in cancer treatment are widely known to cause hair loss. Hair normally grows back once the medicine is stopped.
Some antidepressants can cause hair loss, as can taking too much vitamin A. Hormonal medicines, particularly testosterone, can induce male or female-pattern hair loss. Cancer was treated with a cancer medication called nivolumab.
Between 1% and 2% of people who receive this cancer therapy develop alopecia areata or alopecia universalis (complete hair loss). Hair loss commonly begins a few months after starting nivolumab.
Your doctor may refer to your hair loss as nivolumab-induced alopecia areata. While experiencing patchy or full hair loss might be stressful, it is a healthy indication. It usually indicates that the cancer medicine is effective. If hair loss affects you, a board-certified dermatologist can treat it while you continue to take nivolumab.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata can affect people of any colour or gender and can start at any age. However, most people develop it in their teens, twenties, or thirties. While anyone can get alopecia areata, dermatologists and other experts have discovered that some people are more susceptible. You are at higher risk if you have:
A close blood relative with this hair loss: Alopecia areata, can be inherited through families. People who have alopecia areata at an early age are more likely to have a blood relative with the illness. If you have a family history of alopecia areata, you may inherit particular genes that enhance your chances of having the condition.
Many of these genes influence how the immune system functions. It is vital to understand that you can inherit these genes but never get alopecia areata.
Psoriasis, thyroid disease, and vitiligo are autoimmune illnesses associated with alopecia areata. Having one of these autoimmune diseases may put you at risk of developing alopecia areata, another autoimmune disease.
Asthma, hay fever, or atopic dermatitis: Research indicates that having one of these disorders increases your risk of developing alopecia areata. Cigarette smokers who have smoked for ten years or more and smoke more than five cigarettes per day are at a higher risk of developing alopecia areata, according to several studies.

The danger is greatest for those who have been smoking for more than ten years and consume five or more cigarettes each day. It is not quite clear why smoking cigarettes increases the risk. We know that smoking causes inflammation within the body. The inflammation may raise the possibility that a person’s immune system will assault hair follicles.
Cigarette smokers who have smoked for ten years or more and smoke more than five cigarettes per day are at a higher risk of developing alopecia areata, according to several studies. The danger is greatest for those who have been smoking for more than ten years and consume five or more cigarettes each day.
It is not quite clear why smoking cigarettes increases the risk. We know that smoking causes inflammation within the body. The inflammation may raise the possibility that a person’s immune system will assault hair follicles.
Scalp Infections Causes Hair Loss in Men
Scalp infections are caused by bacteria or fungi that penetrate the hair follicles or scalp skin. They can cause numerous skin rashes and hair loss. The treatment for scalp infections will differ according to the cause. For instance:
Folliculitis is an infection that causes one or more hair follicles to become inflamed and swollen. Bacteria are the most prevalent cause, however, it can also be caused by viruses, parasites, or fungi. Scalp folliculitis causes tiny, itchy bumps to grow on the scalp, particularly noticeable on the frontal hairline.
There may be many or few lesions (skin abnormalities). They are frequently irritating and become painful, sensitive, and crusty. The specific aetiology of scalp folliculitis is unknown. When hair follicles become contaminated with germs, it is often seen as an inflammatory reaction.
Fungal infection: Fungus can occasionally cause scalp infections, and Candida and Malassezia are two types of yeast that can cause them.
Symptoms of a Candida yeast infection on the scalp may include:
- Crusts on the scalp that could.
- lead to hair loss.
- Purple or red spots of skin.
- White flaky scales on the scalp.
- Red and itchy patches of skin.
- Pustules full of pus that resemble pimples .
Antifungal drugs like ointments, shampoos, and foams treat fungi infections.

Ringworm (Tinea Capitis): Ringworm is a fungal condition that can affect skin anywhere. It generates a circular rash that looks like a ring. Ringworm on the scalp (tinea capitis) can cause symptoms such as:
- A scaly, round bald patch
- Itching in the affected area.
- Redness
- Skin cracked
- A kerion (swelled, pus-filled sore)

Chronic Illnesses
Lupus erythematosus and irritable bowel syndrome are two autoimmune disorders that can damage your hairline. Hair loss is one of the most prevalent symptoms of SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), with up to half of patients suffering it at some point throughout their illness.
Diabetes is another chronic disease and does not only require you to avoid sweets. Insulin resistance can result in various adverse effects, including hair loss. Insulin is found in hair follicles and may regulate androgen metabolism and the hair development cycle, contributing to male pattern baldness. Diabetes can also cause the miniaturisation of hair follicles (when they shrink).
Aging Causes Hair Loss in Men
It is usual to find some hairs in your brush or bathroom sink daily. However, if that number appears to be increasing and you notice your hair looks thinner than it used to, the ageing factor may be to blame.
As we age, the number of hair follicles in the growth phase reduces, making our mane less dense. Individual hair strands begin to reduce in diameter, giving the illusion of thinner hair.
These changes are common and can impact anyone. For those assigned male at birth (AMAB), the alterations sometimes manifest as a receding hairline. In some circumstances, aging-related variables (or factors that grow more likely with age) exacerbate or accentuate hair thinning.
What are The Psychological Effects Impacts of Hair Loss in Men
Most studies demonstrate that patients with alopecia have higher levels of anxiety and sadness than controls. They also have low self-esteem, a reduced quality of life, and a negative body image. Those who lose their brows and eyelashes may experience issues with identity and identity change because these traits assist in defining a person’s face.Hair loss can be viewed as an aberration and a failure to comply with societal norms of physical appearance, with the ability to distinguish persons in their own and others’ estimations. People can suffer from severe self-esteem issues. One weakness of the study is that the link between alopecia and depression or anxiety may be obscured by stressful life circumstances that cause both alopecia and depression or anxiety.
Treatment Options and Preventative Measures of Hair Loss in Men
Hair loss can be distressing, but several effective treatments and preventative strategies help men manage and reverse this condition. Numerous strategies, from medical treatments to lifestyle changes, exist to encourage healthy hair development and reduce further loss.

Medical Treatments
Topical minoxidil, which is FDA-approved for treating hair loss, is available over the counter. However, oral minoxidil is considered an “off-label” use and requires a prescription. Healthcare providers have the authority to prescribe off-label medications if they believe they are the best course of therapy for a particular patient.
The most prevalent side effect is hypertrichosis (excess hair growth on the face or body).
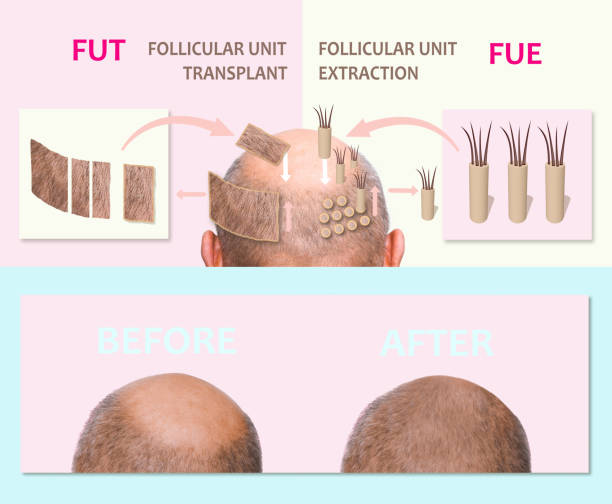
Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery involves transferring hair follicles from one body part to another where hair is thinning or has been gone. Follicles that produce hair are extracted from the sides or rear of the head. This surgical method is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness, a common problem in men. There are two types of hair transplant procedures: follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit transplantation (FUT). FUE is a minimally invasive treatment that extracts individual hair follicles from the donor area and implants them into balding or thinning areas. This procedure results in tiny, practically undetectable scars and a faster healing time than FUT.
FUE is popular because of its precision and ability to provide natural-looking outcomes. Conversely, FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the donor location to harvest and transplant individual hair follicles. While this procedure may result in a linear scar, it enables the transplantation of many grafts in a single session, making it appropriate for severe hair loss situations. FUT demands a longer recuperation time than FUE. Both methods play a big role in hair restoration.

Lifestyle Changes to Help Men Overcome Hair Loss
A well-balanced diet rich in protein and iron can help keep your hair healthy and strong. Protein, which makes up the majority of hair follicles, is also found in foods like chicken, eggs, Greek yogurt, and beef. Protein also contains iron, which aids the body’s ability to transport oxygen to hair-growing cells. When the body doesn’t get enough protein, the consumed protein is allocated to essential body functions, which don’t include hair growth. The most prevalent side effect is hypertrichosis (excess hair growth on the face or body).
Avoid Most Hair Styling Products Advertised For Hair Loss Solution
It’s also a good idea to use less hair styling and product. Shampoos that claim to promote hair growth are usually not worth the money because they do not stay in the hair long enough to reach the follicles.
Shampoos designed to address dandruff and eczema, which can lead to hair loss, may be useful in treating those conditions but not hair loss itself.

Avoid Mental Stress
The treatment for this is simple: manage stress and understand that the ailment is nearly always temporary and should resolve without long-term implications within a few weeks to months; if not, consult a doctor.
Home Remedies and Natural Solutions for Hair Loss
The following are commonly used hair loss remedies for men. At least one study revealed that rosemary oil promotes hair development like the over-the-counter hair-growing medicine minoxidil, also known as Rogaine. According to Ashton, the oil collected from the rosemary plant can be applied directly to the scalp and massaged. Peppermint oil has been found in animal experiments to promote hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp. Peppermint oil must be diluted with another oil before applying and massaging it into the scalp. Simply massaging your scalp might help enhance hair thickness. The procedure works by increasing blood flow to the scalp.

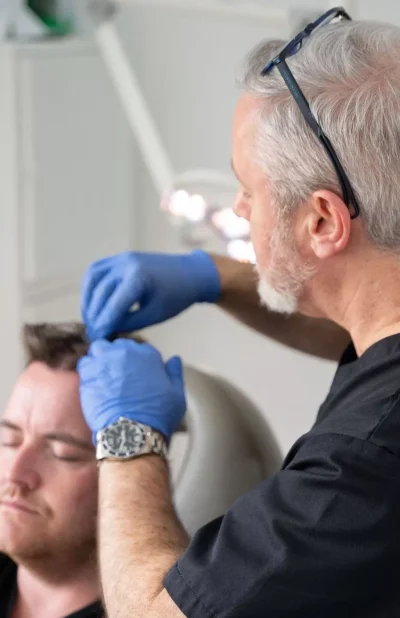
Cosmetic Solutions For Hair Loss in Men
A wig is a hair item worn on the scalp to alter your hair’s appearance or conceal hair loss. Men’s baldness wigs are also known as toupees, hairpieces, hair prosthesis, or non-surgical hair replacement systems. Many low-cost wigs are synthetic hair, whereas high-end wigs are frequently made of genuine hair and custom-fitted to sit naturally on the wearer’s scalp.
Wigs are not meant to stop hair loss or cause any regrowth of your natural hair, but they will beautifully mask the bald scalp and make you comfortable.
When to See a Doctor About Your Hair Loss
If you experience unexplained hair loss, see a healthcare expert to discover the underlying cause and the best course of therapy. During your appointment, make sure to note any additional strange symptoms you’ve seen, including Symptoms may include:
- Exhaustion
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Bowel motion changes
Don’t forget to mention to your doctor about:
- Rashes or skin abnormalities on your scalp or body
- Recent medical treatments.
- Changes to your diet and nutrition
- Any new immunisation or medicine
Reclaim Your Confidence with Merchant City Medical Group
For many men, going through hair loss can be difficult but it doesn’t have to be permanent or define your self-esteem. Understanding the root causes is the first step toward finding the right solution. At Merchant City Medical Group , we specialize in advanced FUE hair transplant procedures that offer a natural, long-lasting solution tailored to your needs. With our expert team and flexible financial assistance options, regaining your full head of hair has never been more accessible.
Located in the UK and serving clients across Europe, we are dedicated to helping you look and feel your best. Don’t let hair loss hold you back—schedule your free consultation today and take the first step toward a renewed sense of confidence with Merchant City Medical Group.